Highlights of Previous Month
1. Software Architecture Pattern - Layered Architecture
2. How Enterprise Applications Exchange Data Using Messaging
3. Microservices Design Pattern - Event Sourcing Pattern
4. Improve API Performance 🚀
5. Distributed System Learning Roadmap
APIs are the backbone of modern applications, enabling communication between services and delivering data seamlessly. But when API performance is slow, it can impact user experience, reduce productivity, and increase server costs. Let's explore some techniques to improve API performance, with examples and practical tips along the way! 🛠️
1. Optimize Database Queries with Indexing 📊
Slow database queries are a common bottleneck for APIs. Using indexes on frequently queried fields can significantly boost query performance, reducing API response time.
Example:
Suppose your API retrieves user data by user_id frequently. Adding an index to user_id can speed up these queries.
CREATE INDEX idx_user_id ON users(user_id);This will reduce query time, making the API faster for requests involving this field.
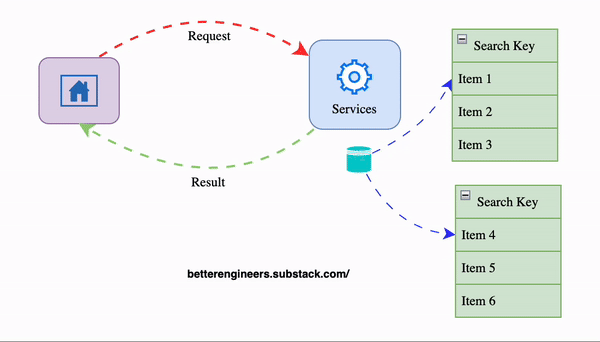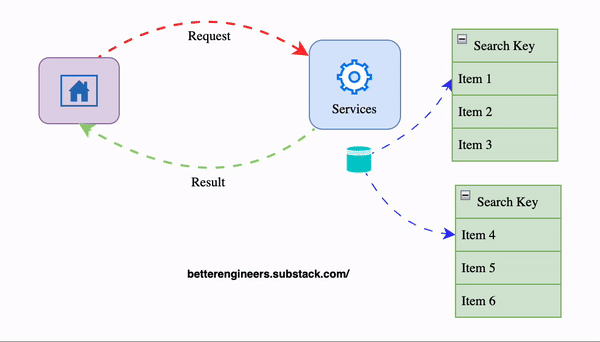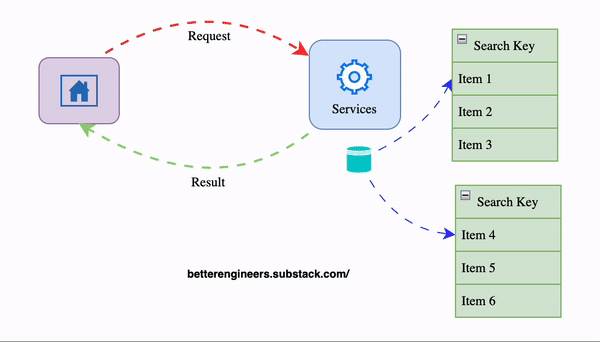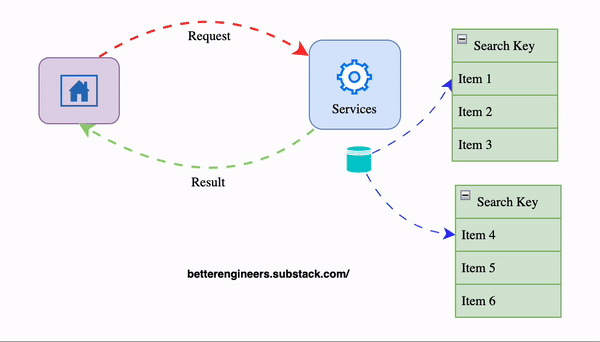
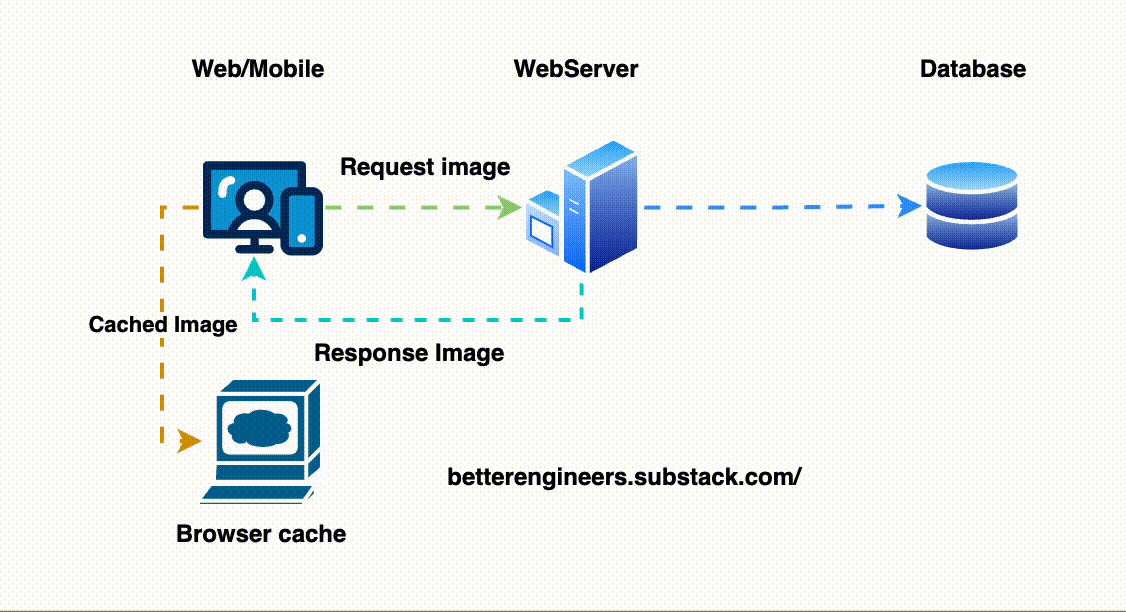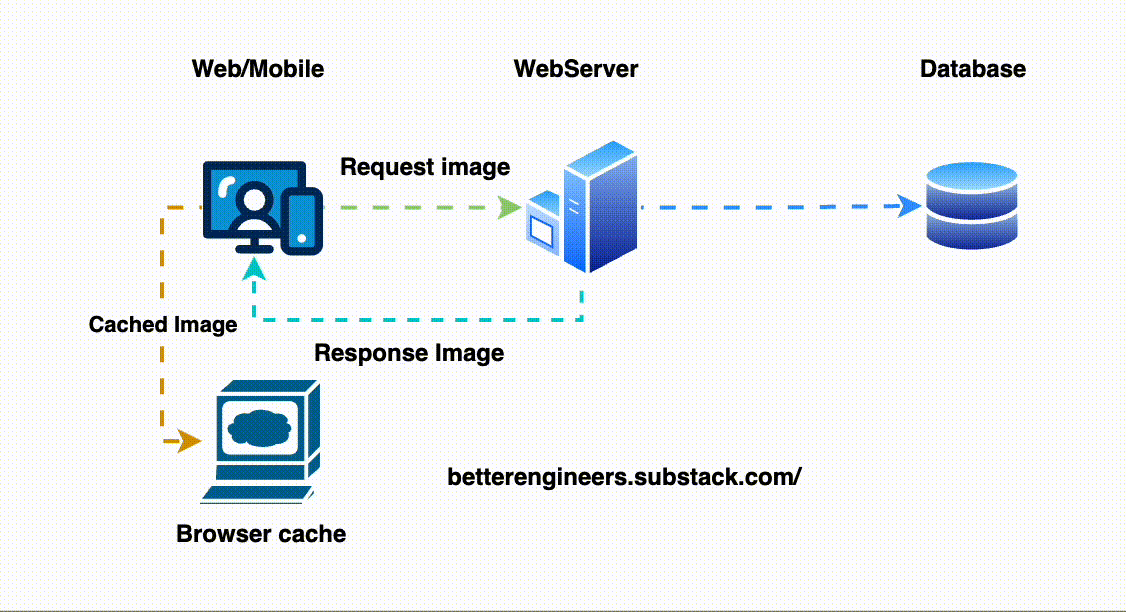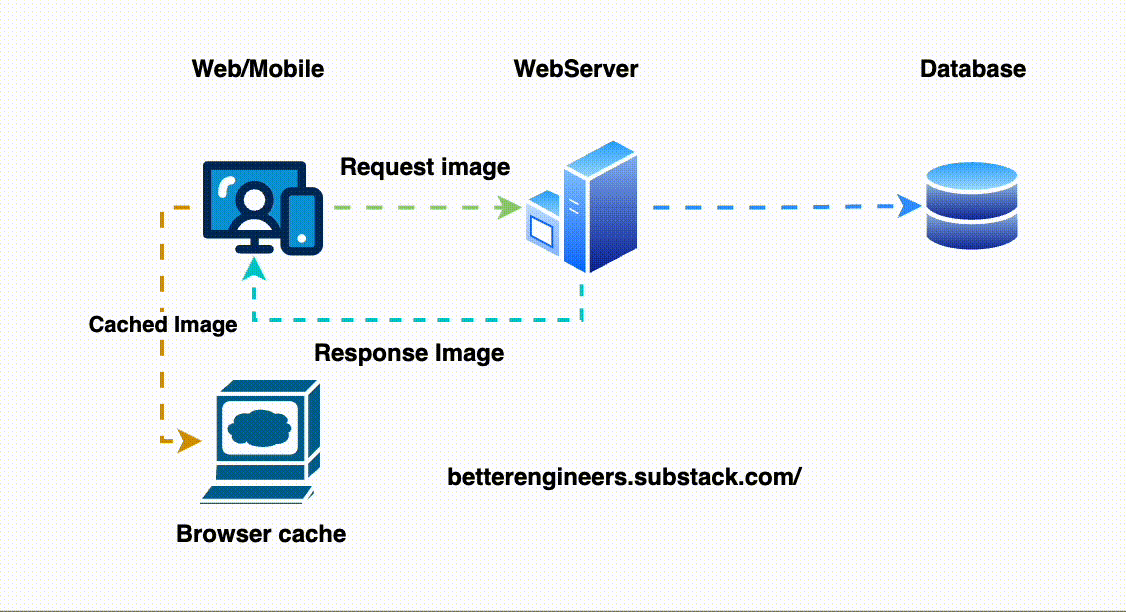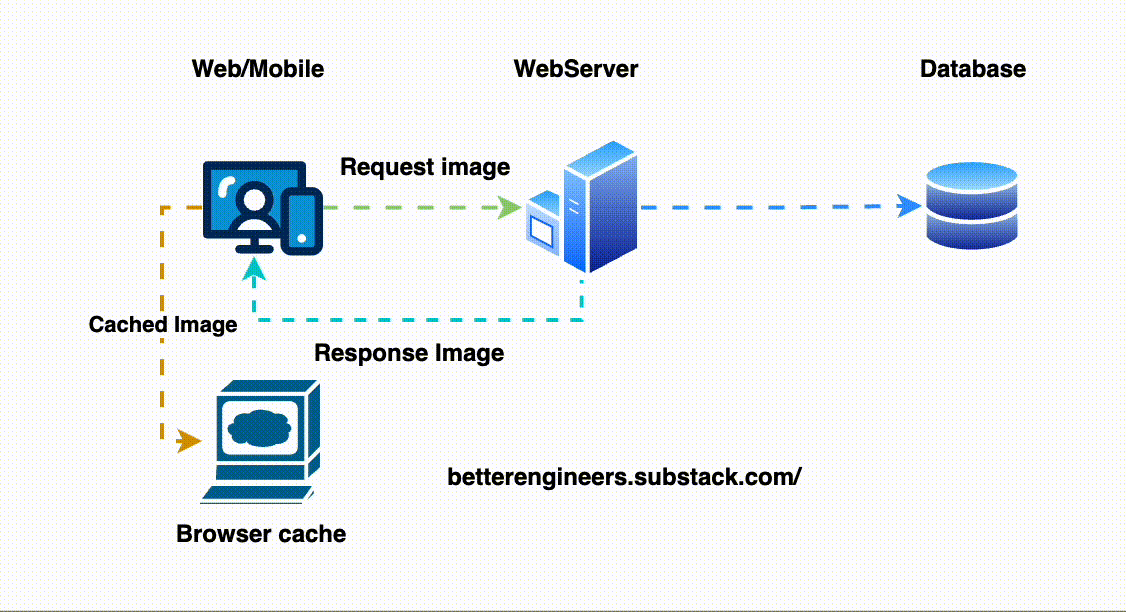
2. Implement Caching to Minimize Load on the Database
Caching stores a temporary copy of the response, allowing the API to return results more quickly without repeatedly querying the database. This is especially helpful for data that doesn’t change frequently.
Example with Redis Caching in Python:
import redis
cache = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379)
# Check if data is in cache
user_data = cache.get("user_123")
if not user_data:
# Fetch from database if not in cache
user_data = fetch_user_from_db(user_id=123)
# Save in cache for future requests
cache.set("user_123", user_data, ex=60*60)
# Cache for 1 hourHere, the user_123 data will be served from cache if it’s available, avoiding an unnecessary database hit.
Limited Offer 20% Off
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Better Engineers to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.